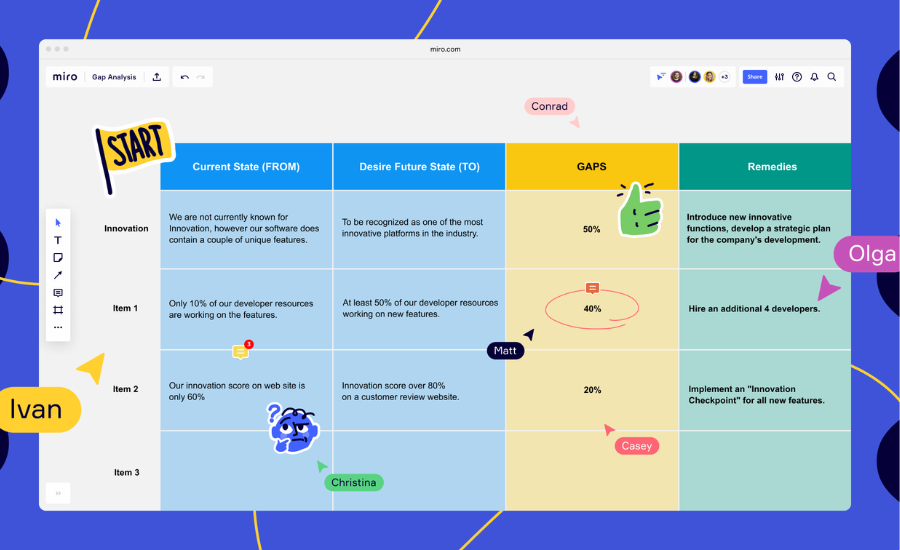
A gap analysis template is a valuable tool used to assess the difference or “gap” between the current state of a project, process, or organization and its desired future state. It provides a structured approach to identify areas of improvement, uncover potential challenges, and develop strategies to bridge the gap effectively. By utilizing a gap analysis template, organizations can systematically evaluate their current state, define their future objectives, and develop an actionable plan to close the gaps effectively.
What are gap analyses and examples?
Gap analysis is a strategic tool used to assess the discrepancies or gaps between the current state of a project, process, or organization and its desired future state. It involves comparing the existing conditions, performance, or capabilities with the desired goals or objectives, and identifying areas where improvements are needed.
Gap analysis can be applied in various contexts, such as:
Performance Gap Analysis:
This type of analysis is commonly used in businessess and organizations to evaluate the difference between current performance levels and desired performance goals. It helps identify areas where performance falls short and where improvements are necessary to reach the desired outcomes.
Example:
A company sets a sales target of $1 million for the year but achieves only $700,000 in sales. The gap analysis would reveal a performance gap of $300,000 that needs to be addressed.
Skills Gap Analysis:
This analysis is focused on assessing the knowledge, skills, and competencies of individuals or teams in relation to the required skills for a particular role or task. It helps identify gaps in skills and training needs.
Example:
A software development team conducts a skills gap analysis and identifies that their team lacks expertise in a specific programming language required for an upcoming project. They can then plan to provide training or hire new team members with the required skills.
Market Gap Analysis:
Market gap analysis is used to evaluate the difference between customer expectations and the products or services currently offered in the market. It helps businesses identify opportunities for new products or improvements to existing ones.
Example:
A company discovers through market research that there is a demand for a particular type of eco-friendly cleaning product that is not currently available in the market. They can use this information to develop and launch a new product to fill the market gap.
Process Gap Analysis:
Process gap analysis involves assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of existing processes in achieving desired outcomes. It helps identify gaps in process efficiency, compliance, or effectiveness.
Example:
A manufacturing company conducts a process gap analysis and finds that a specific production line is experiencing higher rates of defects and delays compared to the desired benchmarks. The analysis reveals gaps in the process that need to be addressed to improve overall efficiency and product quality.
In each of these examples, a gap analysis provides valuable insights by identifying areas of improvement and guiding decision-making and planning processes to bridge the gaps and move closer to the desired future state.
Gap analysis in Excel
Performing a gap analysis in Excel can be a useful and efficient way to organize and analyze data. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to conduct a gap analysis using Excel:
Step 1: Define the Current State and Future State
- Create two columns in Excel, labeling them “Current State” and “Future State.”
- List the relevant factors, metrics, or objectives in each column, representing the current and desired future state.
Step 2: Gather Data and Assess the Current State
- Collect data or information related to the factors or metrics in the “Current State” column.
- Enter the data in the corresponding cells in Excel.
- Perform calculations, if needed, to derive specific metrics or values for each factor.
Step 3: Assess the Future State
- Similarly, gather data or information related to the factors or metrics in the “Future State” column.
- Enter the data in the corresponding cells in Excel.
Step 4: Calculate the Gap
- Create another column in Excel, labeling it “Gap.”
- Use formulas to calculate the gap between the current state and future state for each factor. The formula typically involves subtracting the current state value from the future state value.
Step 5: Analyze the Gap
- Review the gap values in the “Gap” column to identify areas of improvement.
- Sort or filter the data to prioritize the gaps based on their significance or impact.
- Use charts or graphs to visually represent the gaps and their magnitudes.
Step 6: Develop Action Plans
- Create a new column in Excel, labeling it “Action Plan.”
- For each identified gap, brainstorm and enter action steps or strategies to bridge the gap.
Step 7: Assign Responsibilities and Set Timelines
- Create additional columns in Excel to assign responsible parties, set deadlines, and allocate resources for each action step.
Step 8: Monitor Progress
- Regularly update the status and progress of each action step in Excel.
- Use conditional formatting or progress indicators to track the completion of tasks.
Step 9: Review and Revise
- Periodically review the gap analysis in Excel to assess progress and identify any changes or adjustments required.
- Make updates to the data, action plans, or timelines as needed.
Using Excel for gap analysis provides a structured and organized way to document and track the gaps, action plans, and progress over time. It allows for easy data manipulation, analysis, and visualization, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and effectively bridge the identified gaps.
Write a gap analysis
Gap Analysis: Current State vs. Future State
Introduction:
This gap analysis aims to assess the differences or “gaps” between the current state and the desired future state of [project, process, or organization]. By conducting this analysis, we can identify areas of improvement and develop strategies to bridge the gaps effectively, ultimately moving towards the desired outcomes.
Define the Current State:
Outline the current situation, processes, performance metrics, and resources in this section. Include relevant data and information that accurately represents the current state of the project, process, or organization.
Define the Future State:
Clearly articulate the desired outcomes, goals, or objectives that you intend to achieve. This section should provide a comprehensive understanding of the expectations for the project, process, or organization in its ideal state.
Identify the Gaps:
Compare the current state with the future state to identify gaps or discrepancies. This step involves a thorough analysis of the data, performance metrics, stakeholder feedback, industry benchmarks, or any other relevant information. Highlight the gaps between the current and desired states for each factor or metric.
Perform Root Cause Analysis:
Dig deeper into the identified gaps to uncover the underlying causes or factors contributing to them. Analyze the reasons why these gaps exist and determine the key drivers behind them. This step is crucial in understanding the root causes and providing insights for developing effective strategies.
Develop Action Plans:
Based on the identified gaps and root cause analysis, outline specific actions, initiatives, or projects to bridge the gaps. Each action plan should be clearly defined, including a timeline, responsible parties, required resources, and milestones to track progress. Ensure that the action plans are feasible and aligned with the overall objectives.
Implement and Monitor:
Execute the action plans and closely monitor the progress. Regularly track the implementation of the action steps, measure key performance indicators, and assess the effectiveness of the strategies. Make adjustments as necessary and ensure that the progress is aligned with the desired outcomes.
Conclusion:
This gap analysis has provided a comprehensive assessment of the gaps between the current state and the desired future state. By identifying these gaps and implementing the action plans, we can proactively work towards closing the discrepancies and achieving the desired outcomes. Regular monitoring and evaluation will allow us to track progress and make necessary adjustments to ensure success.
3 fundamental components of a gap analysis
The three fundamental components of a gap analysis are:
Current State Assessment:
This component involves thoroughly examining and assessing the current state of the project, process, or organization. It includes gathering relevant data, analyzing performance metrics, reviewing existing processes, identifying strengths and weaknesses, and understanding the current capabilities and resources. The purpose of this assessment is to establish a clear understanding of the starting point and to identify the gaps between the current state and the desired future state.
Future State Definition:
This component focuses on defining the desired outcomes, goals, or objectives that the project, process, or organization aims to achieve. It involves envisioning the ideal future state and clearly articulating the expectations and targets. Defining the future state provides a benchmark against which the current state can be compared, enabling the identification of gaps and the formulation of strategies to bridge them.
Gap Identification and Analysis:
This component involves comparing the current state with the future state to identify and analyze the gaps or discrepancies. It entails a comprehensive evaluation of the differences between the two states, considering various factors, performance metrics, stakeholder feedback, industry standards, or best practices. Gap identification and analysis provide insights into the areas where improvements are needed and highlight the specific gaps that need to be addressed.
Is a SWOT analysis a gap analysis?
No, a SWOT analysis is not the same as a gap analysis, although they can be complementary and used in conjunction with each other. A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool that evaluates an organization’s internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. It involves identifying and analyzing the organization’s strengths and weaknesses (internal factors) and opportunities and threats (external factors) in relation to its objectives or a specific situation. The analysis helps organizations understand their current position, capitalize on their strengths, address weaknesses, leverage opportunities, and mitigate threats.
On the other hand, a gap analysis focuses specifically on assessing the gaps or discrepancies between the current state and the desired future state. It compares the existing conditions, performance, or capabilities with the desired goals or objectives, and identifies areas where improvements are needed. The analysis helps identify the specific gaps that need to be addressed and develops strategies to bridge those gaps effectively. While a SWOT analysis provides a broader view of the organization’s internal and external factors, a gap analysis zooms in on specific areas of improvement and focuses on identifying and addressing gaps to achieve desired outcomes. In some cases, a gap analysis may be conducted as part of the SWOT analysis to assess the gaps in relation to the identified strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Types of gap analysis
There are several types of gap analysis that can be conducted depending on the specific context and objectives. Here are some common types:
Performance Gap Analysis:
This type of gap analysis focuses on assessing the gaps between current performance levels and desired performance goals. It involves comparing actual performance metrics, such as sales figures, productivity levels, customer satisfaction ratings, or key performance indicators, with the target or benchmark values. The analysis helps identify areas where performance falls short and improvements are necessary to bridge the performance gap.
Skills Gap Analysis:
Skills gap analysis is used to assess the gaps between the current skills and competencies of individuals or teams and the skills required for a particular role or task. It involves identifying the knowledge, skills, and abilities needed for successful performance and then comparing them with the existing skill sets. The analysis helps determine training needs, recruitment requirements, and development strategies to bridge the skills gap.
Market Gap Analysis:
Market gap analysis is focused on assessing the gaps between customer expectations and the products or services currently offered in the market. It involves gathering market research data, customer feedback, or competitive analysis to understand customer needs, preferences, and trends. The analysis helps identify opportunities for new products or improvements to existing ones, thereby bridging the gap between customer expectations and current offerings.
Compliance Gap Analysis:
Compliance gap analysis is used to evaluate the gaps between current practices and regulatory or legal requirements. It involves comparing existing policies, procedures, and practices with applicable laws, regulations, industry standards, or internal guidelines. The analysis helps identify areas of non-compliance, potential risks, and necessary corrective actions to bridge the compliance gap.
Process Gap Analysis:
Process gap analysis focuses on assessing the gaps between the current process efficiency and effectiveness and the desired benchmarks. It involves analyzing existing workflows, procedures, and process metrics to identify areas of inefficiency, bottlenecks, or deviations from best practices. The analysis helps pinpoint areas for process improvement, streamlining, or optimization to bridge the process gap.
Financial Gap Analysis:
Financial gap analysis is used to evaluate the gaps between actual financial performance and financial targets or objectives. It involves comparing financial data, such as revenue, costs, profitability, or cash flow, with the desired financial outcomes. The analysis helps identify areas where financial performance is falling short and where strategic adjustments or financial management practices are needed to bridge the financial gap.
Gap analysis framework
A gap analysis framework provides a structured approach to conducting a thorough and systematic analysis of the gaps between the current state and the desired future state. While specific frameworks may vary depending on the context and objectives, here is a general framework that can be used as a starting point:
Define the Scope and Objectives:
Clearly define the scope of the analysis and establish the specific objectives to be achieved. This step helps ensure a focused and targeted analysis.
Identify the Current State:
Thoroughly assess and document the current state of the project, process, or organization. Gather relevant data, performance metrics, and information that accurately represents the current situation.
Define the Future State:
Clearly articulate the desired outcomes, goals, or objectives that you intend to achieve. Establish a clear vision of the ideal future state and ensure alignment with organizational goals and stakeholder expectations.
Identify the Factors for Analysis:
Identify the key factors, metrics, or areas that will be analyzed to assess the gaps. These factors should be relevant to the objectives and provide a comprehensive understanding of the current and desired states.
Gather Data and Perform Analysis:
Collect data and information related to the identified factors. Analyze the data to assess the gaps between the current and desired states. Use appropriate analytical tools, techniques, and methods to interpret the data and derive meaningful insights.
Conduct Gap Identification:
Compare the data and analysis results to identify the gaps between the current and desired states for each factor. Clearly document and highlight these gaps, ensuring that they are measurable and quantifiable.
Perform Root Cause Analysis:
Dig deeper into the identified gaps to understand the underlying causes or factors contributing to them. Conduct a thorough root cause analysis to identify the reasons why these gaps exist.
Develop Action Plans:
Based on the identified gaps and root cause analysis, develop specific action plans or strategies to bridge the gaps. Each action plan should be clearly defined, outlining the steps, responsibilities, resources, and timelines required for implementation.
Implement and Monitor:
Execute the action plans and closely monitor the progress. Regularly track the implementation of the action steps, measure key performance indicators, and assess the effectiveness of the strategies. Make adjustments as necessary and ensure that the progress aligns with the desired outcomes.
Review and Revise:
Periodically review the gap analysis to assess progress and identify any changes or adjustments required. Continuously update and refine the analysis based on new information or evolving objectives.
Gap analysis process
The gap analysis process involves a series of steps to systematically assess the gaps between the current state and the desired future state. Here is a general outline of the gap analysis process:
Define the Scope and Objectives:
Clearly define the scope of the gap analysis, including the specific area, project, process, or organization that will be analyzed. Establish the objectives and desired outcomes of the analysis to provide a clear focus.
Identify the Factors or Metrics:
Identify the key factors, metrics, or areas that will be analyzed to assess the gaps. These factors should be relevant to the objectives and provide a comprehensive understanding of the current and desired states. Examples include performance metrics, customer satisfaction, market share, compliance requirements, skills, or process efficiency.
Gather Data:
Collect relevant data and information related to the identified factors. This may involve reviewing existing documentation, conducting surveys, interviews, or observations, and analyzing available data sources. Ensure that the data collected is accurate, reliable, and representative of the current state.
Assess the Current State:
Thoroughly analyze and assess the current state based on the gathered data. Evaluate the performance, capabilities, strengths, weaknesses, and any other relevant aspects related to the identified factors. Document the findings to establish a baseline for comparison.
Define the Future State:
Clearly articulate the desired outcomes, goals, or objectives that you intend to achieve. Establish a clear vision of the ideal future state based on stakeholder expectations, industry best practices, or strategic goals.
Analyze the Gaps:
Compare the current state with the future state to identify and analyze the gaps or discrepancies. Evaluate the differences between the two states for each identified factor. This analysis helps quantify and understand the magnitude of the gaps and provides insights into the areas requiring improvement.
Perform Root Cause Analysis:
Dig deeper into the identified gaps to understand the underlying causes or factors contributing to them. Conduct a root cause analysis to identify the reasons why these gaps exist. This analysis helps identify the specific issues, challenges, or barriers that need to be addressed to bridge the gaps effectively.
Develop Action Plans:
Based on the identified gaps and root cause analysis, develop specific action plans or strategies to bridge the gaps. Define the steps, responsibilities, resources, and timelines required for implementation. Ensure that the action plans are realistic, achievable, and aligned with the desired outcomes.
Implement and Monitor:
Execute the action plans and closely monitor the progress. Track the implementation of the action steps, measure key performance indicators, and assess the effectiveness of the strategies. Regularly review and update the progress, making adjustments as necessary to stay on track.
Review and Continuous Improvement:
Periodically review the gap analysis process to evaluate its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Incorporate feedback, learnings, and new information to refine the analysis and the action plans. Continuously update and adapt the analysis as objectives evolve or new gaps emerge.
Faqs
Q1: What is a gap analysis template?
A gap analysis template is a pre-designed framework or document that provides a structured format for conducting a gap analysis. It typically includes sections and prompts to guide the analysis process, such as defining the current state, identifying the desired future state, assessing gaps, performing root cause analysis, and developing action plans.
Q2: Why should I use a gap analysis template?
Using a gap analysis template offers several advantages. It provides a systematic and organized approach to conducting the analysis, ensures consistency across different analyses, saves time by providing a ready-made structure, and helps in capturing and documenting key information in a standardized manner.
Q3: Where can I find a gap analysis template?
There are several sources where you can find gap analysis templates. You can search online for free or paid templates available on various websites, including business or project management websites. Additionally, software applications or tools related to performance management or strategic planning often include built-in gap analysis templates.
Q4: Can I customize a gap analysis template to fit my needs?
Yes, most gap analysis templates are customizable to some extent. You can modify the sections, headings, or prompts to align with your specific project, process, or organizational context. Customization allows you to tailor the template to your unique requirements and ensures that the analysis addresses the specific factors or metrics relevant to your situation.
Q5: What are some common sections in a gap analysis template?
A typical gap analysis template may include sections such as:
- Introduction: Providing an overview and purpose of the analysis.
- Current State Assessment: Defining and evaluating the current situation, processes, or performance.
- Future State Definition: Articulating the desired outcomes or objectives.
- Gap Identification: Comparing the current and future states to identify gaps.
- Root Cause Analysis: Analyzing the underlying reasons or factors contributing to the gaps.
- Action Plans: Develop specific strategies or initiatives to bridge the gaps.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Outlining steps for executing the action plans and tracking progress.
- Conclusion: Summarize the analysis and key findings.
These sections serve as a starting point, and you can adjust or add sections as needed for your specific analysis.
Q6: Can I create my own gap analysis template?
Absolutely! If you have a preferred format or specific requirements for your analysis, you can create your own gap analysis template from scratch. Consider including sections that align with your objectives, factors to analyze, and reporting format that suits your needs. Creating a custom template allows you to tailor it precisely to your unique situation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a gap analysis template provides a valuable framework for conducting a structured and systematic analysis of the gaps between the current state and the desired future state. It offers several benefits, including consistency, time-saving, and standardized documentation. Whether you choose to use a pre-designed template or create your own, the template can be customized to fit your specific needs and context. It typically includes sections such as current state assessment, future state definition, gap identification, root cause analysis, action plans, and implementation monitoring. By utilizing a gap analysis template, you can effectively identify areas for improvement, bridge the gaps, and work towards achieving your desired outcomes.



